Chain Abstraction: Why is it the Hottest Narrative in Crypto?
Here's all you need to know about it...
Introduction.
The web3 space is ruled by narratives. And where narratives is king, all we need to do is spot them early and buy into the trends they generate. Because in the long run, buying into trending narratives always gives the biggest winners.
Many narratives and trends have come and gone over the past couple of years – DeFi summer, NFTs, memecoins… Many more are also being spun out of the web that is web3, such as DePIN, LSDs, RWAs, etc. But which will gain steam and be the hottest narrative that’ll shape this bull season?

If I were asked, I’d say Chain Abstraction is one narrative sparking up a fiery hot trend that will change the entire crypto landscape. Here’s why I believe so.
The Current Scalability Problem in The Web3 Space.
While the crypto space has seen tremendous growth since Bitcoin went mainstream, it has not achieved its main goal as of yet; the goal being widespread adoption.
Web3 is meant to be an improvement on web2, but it’s still much less popular than web2. A Consensys survey last year showed that just around 24% of respondents globally are aware of the concept of web3.
The world of web3 is still a niche field, open to just a select few people who can handle the complexities of navigating various blockchain networks, and understand the technicalities of the space.
But should the crypto world be that technical?
The Car, and the Engine Under its Hood (A Story).
For thousands of years, the horse had been a premier means of transport. It stood tall and majestic when groomed, its skin glistening under the light of the sun. And when it cantered or galloped, it made for such a beautiful sight.
But then in the late 1800s, the car was invented. And less than a decade later, horses entirely vanished from the street. But why did the car completely phase out the use of horses in just under a decade? The answer: functionality.
You see, beneath the shiny hood of the car lay an engine; a metallic masterpiece of small intricate parts assembled to achieve one function – powering the automobile. But the truth is, no one cared. All people cared about was that the car took them where they wanted faster than the horse did. No one cared about some noisy box sitting beneath the hood.
And that’s how people interact with technology. They just want to see it work, they don’t care about the mechanism behind it.
So, what then is chain abstraction?
As the blockchain space grew and evolved, various blockchain networks sprung up. Bitcoin was the pioneer, and soon we had Ethereum, Solana, XRPL (Ripple’s Ledger), and on and on.
Added to this, many other networks began to build on these existing networks which resulted in Layer 2 (L2) chains like Arbitrum, Polygon, and the like. These various networks had their numerous crypto tokens used as gas fees; in addition, to move assets from one to another, you needed to bridge the assets.
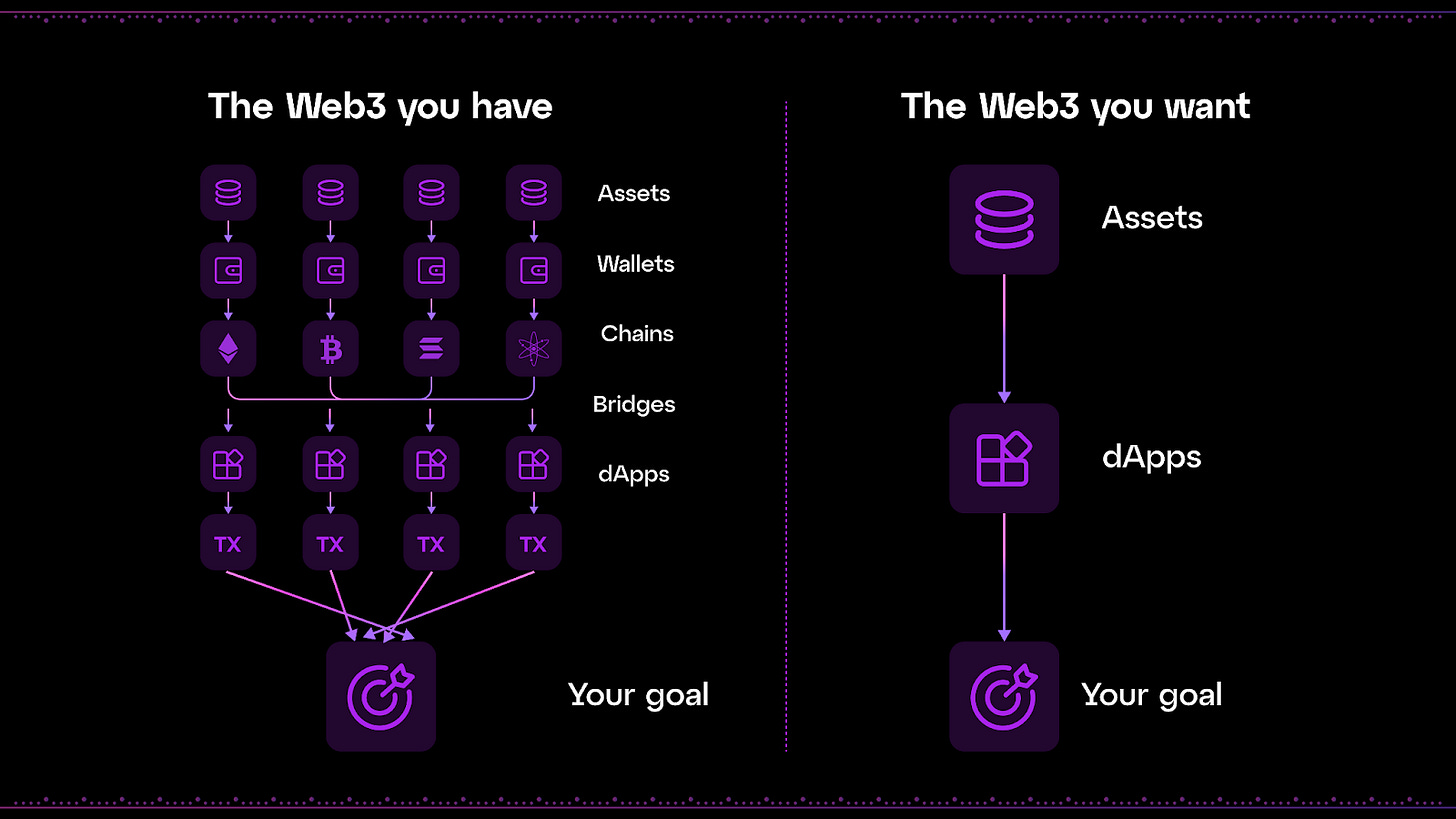
All these resulted in two major problems:
A very complex user experience for people, especially when they perform cross-chain interactions.
Fragmented liquidity, and users. Liquidity is tied to each various blockchains, and so people want to interact more with blockchains having higher liquidity. This results in users, and liquidity being split across different blockchains.
How to solve this problem? That’s where chain abstraction comes in!
Note that abstraction in itself isn’t a new concept; it’s a term that’s been commonly used in computer science and has been defined as:
“The simplification or removal of technical complexities from the user’s experience, producing technologies which exist to hide such details and processes. These complexities are still at play, yet are invisible to the user”.
There’s abstraction at play in virtually every technology in use today. Take your phone for example, to place a phone call, you just have to dial the number and the recipient sees the call. But for the call to have happened, complex routing and switching protocols had been at work, albeit in the background, to ensure the call went through.
So, chain abstraction is a concept that was conceived in a bid to ensure a more enjoyable and seamless user experience for every person who interacts with the blockchain. The idea behind it is to remove the complexities of having to navigate different blockchain networks and allow people to send or receive tokens from different networks seamlessly.
Here’s how Chain Abstraction should work:
If a user, say Tom, wants to interact with the blockchain, he should be able to do it without even worrying about which blockchain network houses his assets and which network he wishes to interact with.
Imagine Tom having no fear of losing his assets because he sent crypto that was developed on Solana to his friend’s Ethereum wallet address; because as he sends such crypto, the app’s infrastructure bridges that crypto to the Ethereum network and then sends it to the recipient’s wallet.
In fact, let’s take it a step further. Imagine the concept of “wallet addresses” vanishing into thin air. Instead, an app is built and users have their unique IDs with which they can send and receive any and every token, no matter the network it’s built on. Mind-blowing right?
Yes, that should give you an idea of how chain abstraction should work. So, Tom can use one DeFi app to send an Ethereum NFT to someone, receive a Solana NFT from another, and also send Polygon tokens to someone else, all from one app.
Why is Chain Abstraction Important?
So far, the average user experience of anyone performing cross-chain interactions hasn’t been so fantastic.
And this scares away regular humans from being a part of this decentralized world because, to be honest, no one wants to be going through bridges and rollups and switching between multiple networks just to transact on the blockchain.
Aside from the fact that chain abstraction helps create a better user experience, it also unifies liquidity scattered across various blockchains. Liquidity on Ethereum won’t be bound to the Ethereum chain anymore, likewise every other blockchain; it’ll be accessible to everyone.
This will incentivize builders to keep creating applications that will serve users across all blockchains.
In a bid to increase mass adoption, chain abstraction will prove the key to unlocking the potential of a decentralized internet.
End note: On projects trying to abstract the blockchain.
First conceptualized by NEAR Foundation in 2023, chain abstraction has gained steam over the years and has grown to be one of the hottest narratives in the crypto space right now.
Different projects have built and launched products aimed at abstracting the blockchain, notable among them being Particle Network, NEAR Protocol, and the like. Check out top projects building chain abstraction tech here.
A question remains, however; can chain abstraction really become a reality? There are some roadblocks, the first being that blockchain networks are built with different programming languages, and as such, interaction between them is limited.
While bridges can solve this problem, chain abstraction is more than just bridges. There has to be layers of tech framework running behind the scenes to make chain abstraction a reality.
Will chain abstraction ever become a reality? It’s just a matter of time.
Learn More:
What is Chain Abstraction? Arriving at a Formal Definition.


